Abstract
Background:
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitors (PI3KI) are a novel class of drugs that are small molecular inhibitors of various isoforms of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K). Over the past decade, various PI3KI have been approved in follicular lymphoma, marginal zone lymphoma, and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. While Copanlisib inhibits P13K-alpha and P13K-delta isoforms, idelalisib inhibits P13K-delta, duvelisib inhibits PI3K-delta and PI3K-gamma, and the recently approved agent umbralisib targets PI3K-delta and casein kinase 1 epsilon with improved selectivity for the PI3K-delta. All the agents except Copanlisib are given orally. Immune-mediated adverse effects like colitis, marrow suppression with infections, and dermatological toxicities are known complications of PI3KI. We did a retrospective analysis of the adverse effects (AE) of the PI3KI in the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS).
Methods:
FAERS public dashboard is a resource through which information related to AEs of treatments reported to the FDA is made available to the public. We investigated the common immune-mediated, infectious, hepatic, and dermatological toxicities of the three PI3KI, idelalisib, copanlisib, and duvelisib for the years 2018 to March 2021. Umbralisib has not much-reported data in FAERS.
Results:
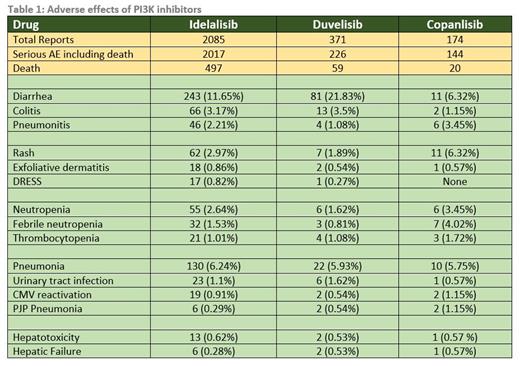
The data regarding various adverse effects are summarized in Table 1. Idelalisib has the most reported data. Diarrhea is reported to be most common with duvelisib (21.83% of total AE). Though diarrhea is common, colitis is uncommon and least reported with copanlisib (1.15%). Among the patients with colitis, death occurred in 27.2% with idelalisib, 15.3% with duvelisib and 50% with copanlisib. Pneumonitis is most reported with copanlisib (3.45%). Among the patients with pneumonitis, death occurred in 34.7% with idelalisib, none with duvelisib and 50% with copanlisib. Rash is most reported with copanlisib (6.32%) and the incidence of serious dermatological toxicity is uncommon in all the 3 drugs. Rates of neutropenia and thrombocytopenia are overall similar between the drugs except for a slightly higher rate in copanlisib including febrile neutropenia. Infections including pneumonia, urinary tract infection, PJP pneumonia, and CMV reactivation are overall comparable between the 3 drugs. Among the patients with various infections, death occurred in 24.1% with idelalisib, 14.5% with duvelisib and 16.9% with copanlisib. The rate of hepatotoxicity is also comparable between the drugs. Among the patients with hepatic failure, death occurred in 33.3% with idelalisib, 100% with duvelisib and copanlisib.
Conclusion:
The overall rates of serious adverse effects are comparable between the 3 PI3KI, though diarrhea is most common with duvelisib, pneumonitis, and rash with copanlisib. As these drugs are mainly used in the relapsed refractory setting, many more years of follow-up are needed to get a better idea of real-world data as we have more experience with these drugs.
Master: Blue Bird Bio: Current holder of individual stocks in a privately-held company.